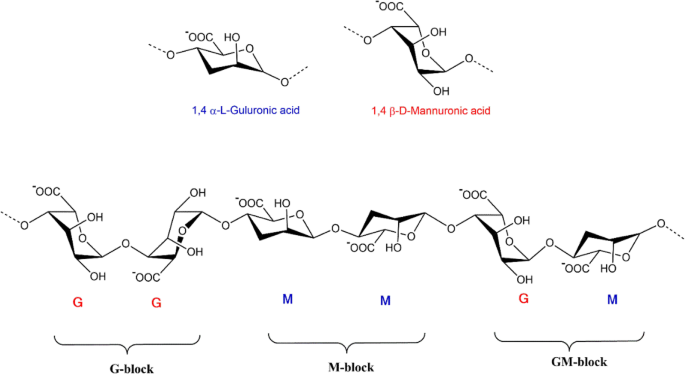
Alginate-based hydrogels as drug delivery vehicles in cancer treatment and their applications in wound dressing and 3D bioprinting, Journal of Biological Engineering
Hydrogels are a three-dimensional and crosslinked network of hydrophilic polymers. They can absorb a large amount of water or biological fluids, which leads to their swelling while maintaining their 3D structure without dissolving (Zhu and Marchant, Expert Rev Med Devices 8:607–626, 2011). Among the numerous polymers which have been utilized for the preparation of the hydrogels, polysaccharides have gained more attention in the area of pharmaceutics; Sodium alginate is a non-toxic, biocompatible, and biodegradable polysaccharide with several unique physicochemical properties for which has used as delivery vehicles for drugs (Kumar Giri et al., Curr Drug Deliv 9:539–555, 2012). Owing to their high-water content and resembling the natural soft tissue, hydrogels were studied a lot as a scaffold. The formation of hydrogels can occur by interactions of the anionic alginates with multivalent inorganic cations through a typical ionotropic gelation method. However, those applications require the control of some properties such as mechanical stiffness, swelling, degradation, cell attachment, and binding or release of bioactive molecules by using the chemical or physical modifications of the alginate hydrogel. In the current review, an overview of alginate hydrogels and their properties will be presented as well as the methods of producing alginate hydrogels. In the next section of the present review paper, the application of the alginate hydrogels will be defined as drug delivery vehicles for chemotherapeutic agents. The recent advances in the application of the alginate-based hydrogels will be describe later as a wound dressing and bioink in 3D bioprinting.

Alginate Based Hydrogel in Drug Delivery and Biomedical Applications
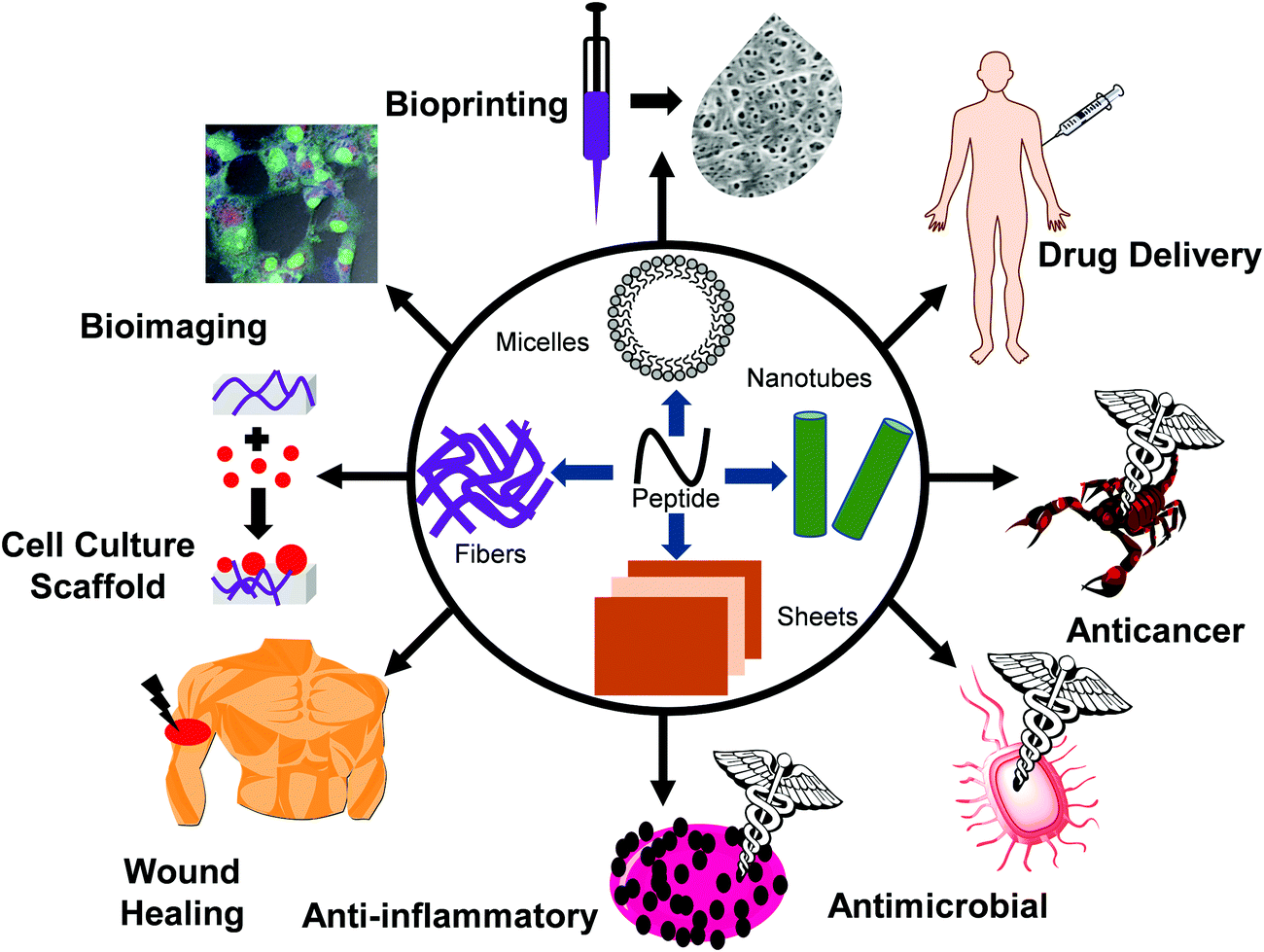
Low molecular weight self-assembling peptide-based materials for cell culture, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, wound healing, anticancer, drug deliv - Soft Matter (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D0SM01136C

Hydrogels Amber bano.pptx

Fabrication and Characterization of Alginate Hydrogels for Control

Alginate-based Hydrogels As Drug Delivery Vehicles In, 49% OFF
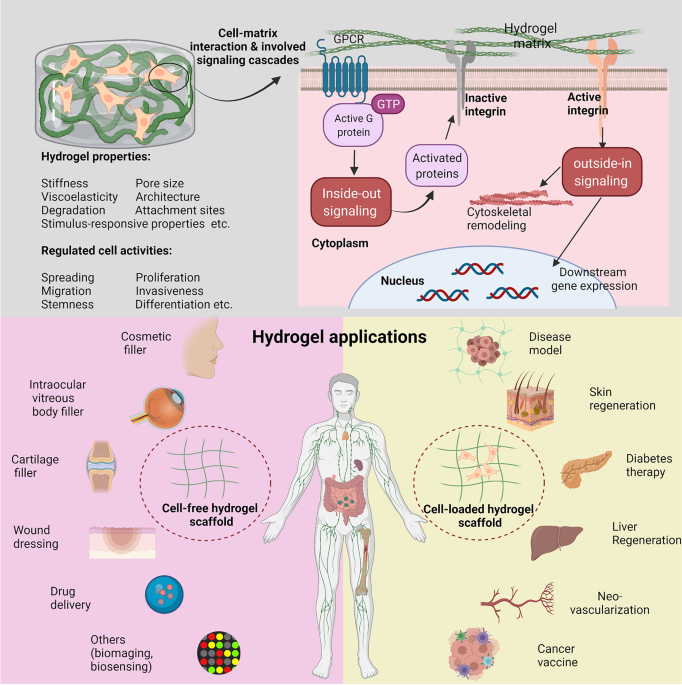
Current hydrogel advances in physicochemical and biological response-driven biomedical application diversity

Bioprinting drug delivery - Wikipedia

Physicochemical Characterization of Nanobiocomposites
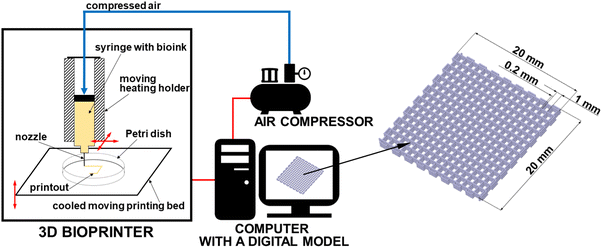
Development of a new 3D bioprinted antibiotic delivery system based on a cross-linked gelatin–alginate hydrogel - Journal of Materials Chemistry B (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/D2TB01268E
Frontiers Hydrogels for Tissue Engineering: Addressing Key Design Needs Toward Clinical Translation

Photoclick Hydrogels Prepared from Functionalized Cyclodextrin and

Alginate-based Hydrogels As Drug Delivery Vehicles In, 49% OFF

Alginate and alginate composites for biomedical applications - ScienceDirect

Ionically and Enzymatically Dual Cross-Linked Oxidized Alginate









