A meta-analysis suggests that tACS improves cognition in healthy, aging, and psychiatric populations

Interventional programmes to improve cognition during healthy and pathological ageing: Cortical modulations and evidence for brain plasticity - ScienceDirect

Lesion network guided delta frequency neuromodulation improves cognition in patients with psychosis spectrum disorders: A pilot study - ScienceDirect

Heriberto Acosta-Velez on LinkedIn: Dementia prevention in memory clinics: recommendations from the European…
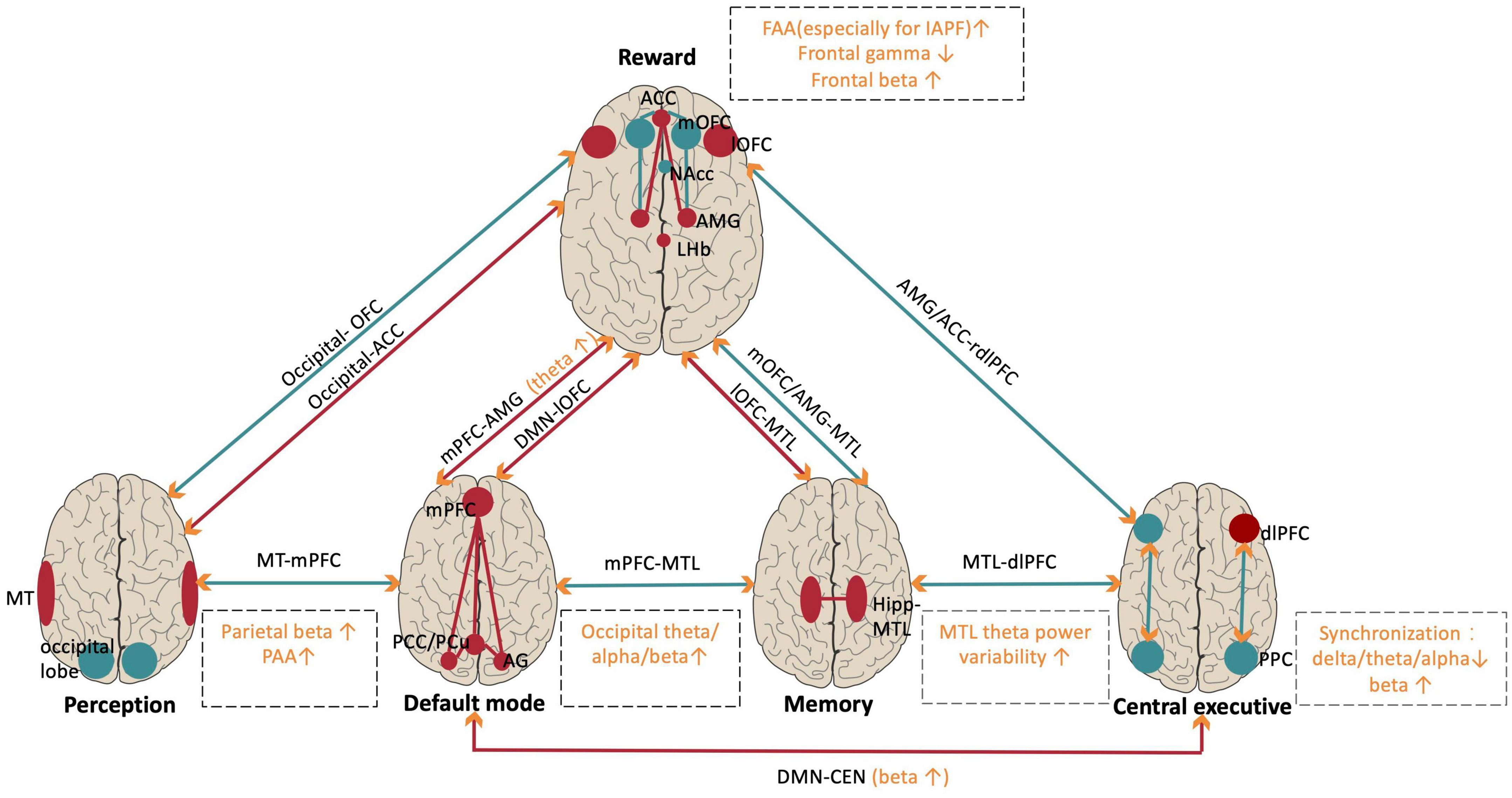
Frontiers Transcranial alternating current stimulation for the treatment of major depressive disorder: from basic mechanisms toward clinical applications

Gamma neuromodulation improves episodic memory and its associated network in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a pilot study - ScienceDirect

A synergetic turn in cognitive neuroscience of brain diseases: Trends in Cognitive Sciences

Dose-dependent effects of transcranial alternating current stimulation on spike timing in awake nonhuman primates

Gamma neuromodulation improves episodic memory and its associated network in amnestic mild cognitive impairment: a pilot study - ScienceDirect

Harald Hampel, MD, PhD, MSc على LinkedIn: A meta-analysis suggests that tACS improves cognition in healthy, aging…
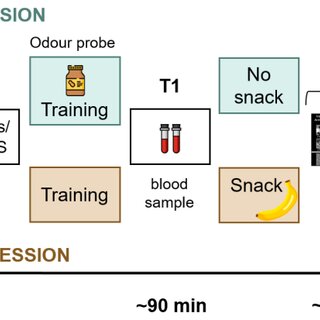
In-phase tACS has no effects on behavioural performance. In this figure

Cognitive and Neuropathophysiological Outcomes of Gamma-tACS in Dementia: A Systematic Review