Welded tuff (western USA), (public display, Geology Departm…
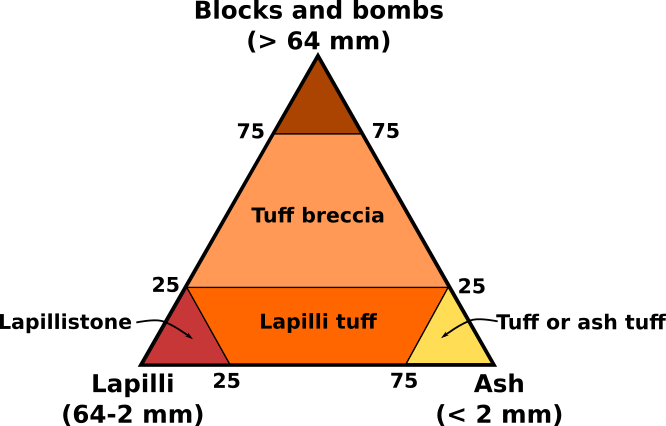
(public display, Geology Department, Wittenberg University, Springfield, Ohio, USA) ----------------------------------- Igneous rocks form by the cooling & crystallization of hot, molten rock (magma & lava). If this happens at or near the land surface, or on the seafloor, they are extrusive igneous rocks. If this happens deep underground, they are intrusive igneous rocks. Most igneous rocks have a crystalline texture, but some are clastic, vesicular, frothy, or glassy. Volcanic tuffs are solidified ash deposits - they form by explosive volcanic eruptions, as do volcanic breccias. Volcanic tuffs lack the abundance of large, angular grains present in volcanic breccias (although I

Minerals, Free Full-Text

Exploring for structurally concealed Carlin-type mineralization: A

Welded tuff (western USA), (public display, Geology Departm…

Search U.S. Geological Survey
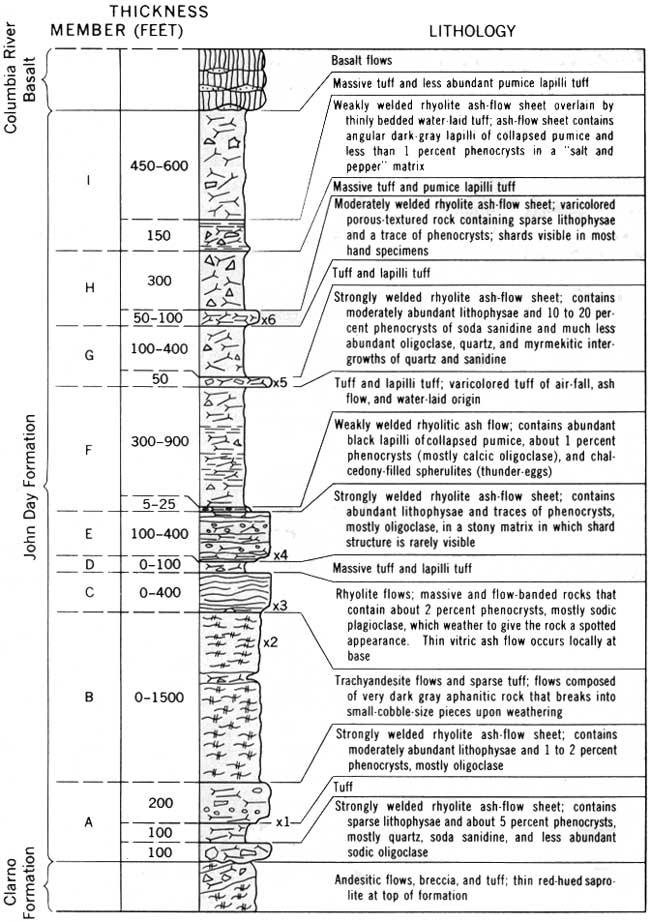
USGS: Geological Survey Bulletin 1161-D (Stratigraphy)
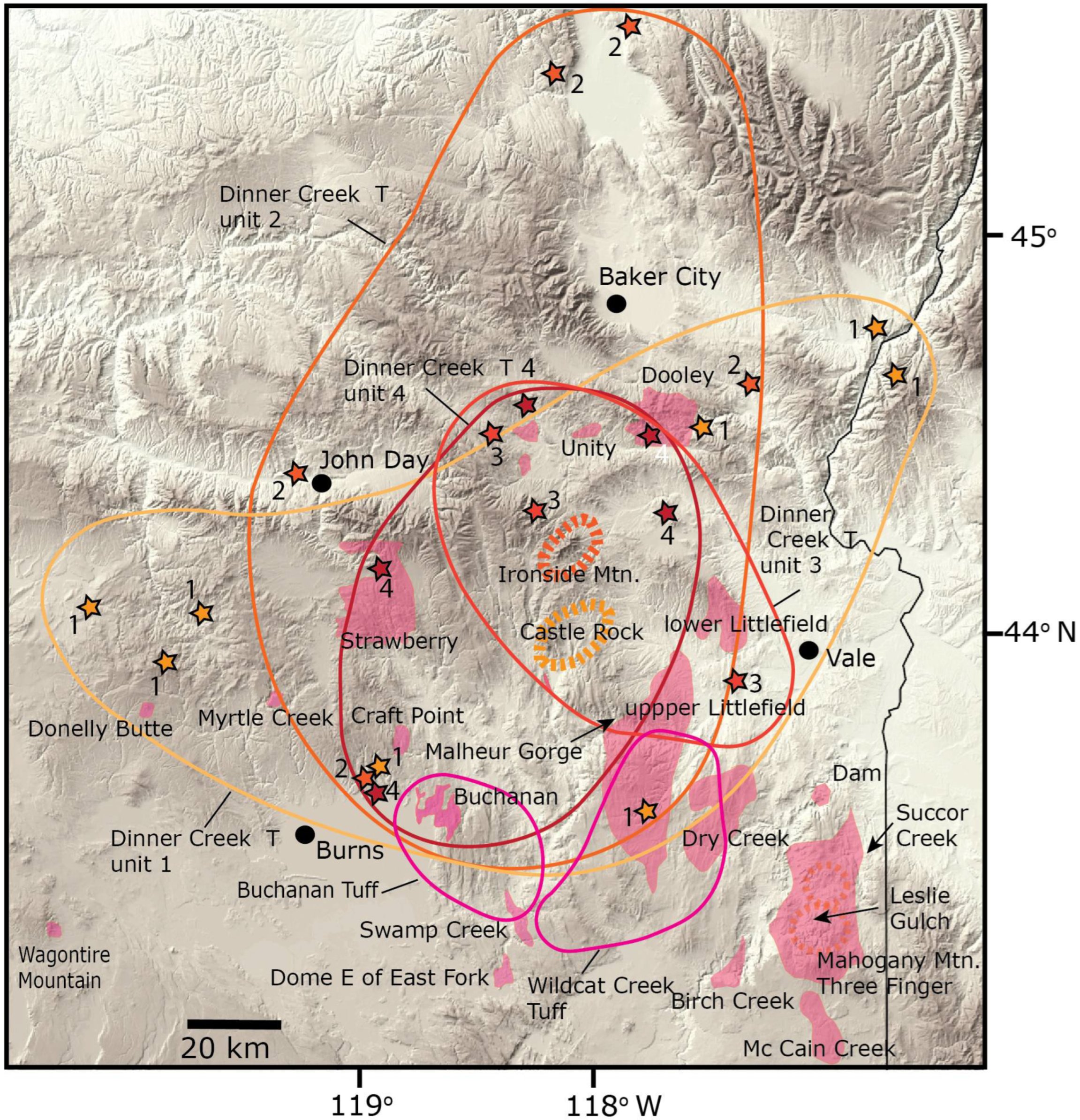
Geosciences, Free Full-Text

James Starnes, RPG - Division Director, Surface Geology Division

Materials, Free Full-Text
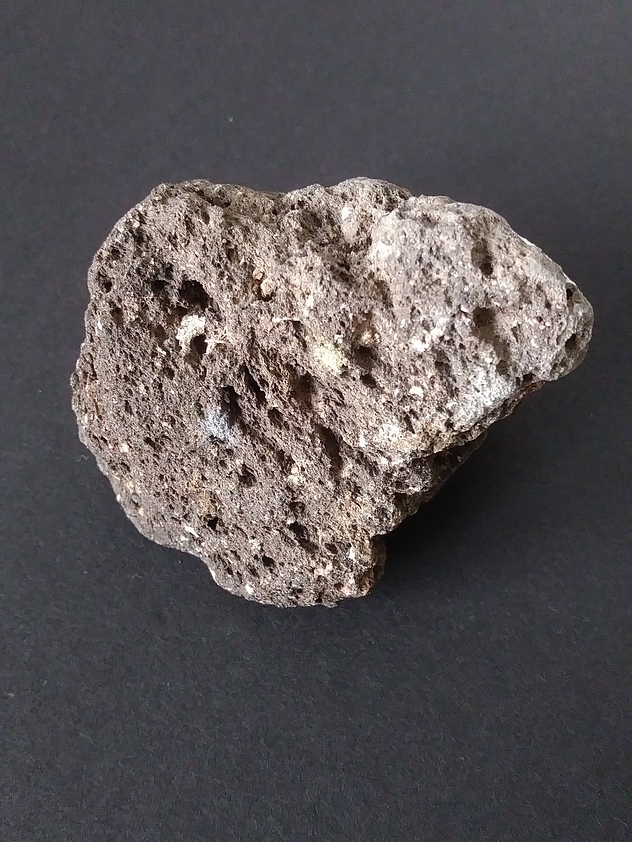

Volcaniclastic rock and sediment: Mineral information, data and

Distinguishing and correlating deposits from large ignimbrite

Tuff - Igneous Rocks

Search U.S. Geological Survey
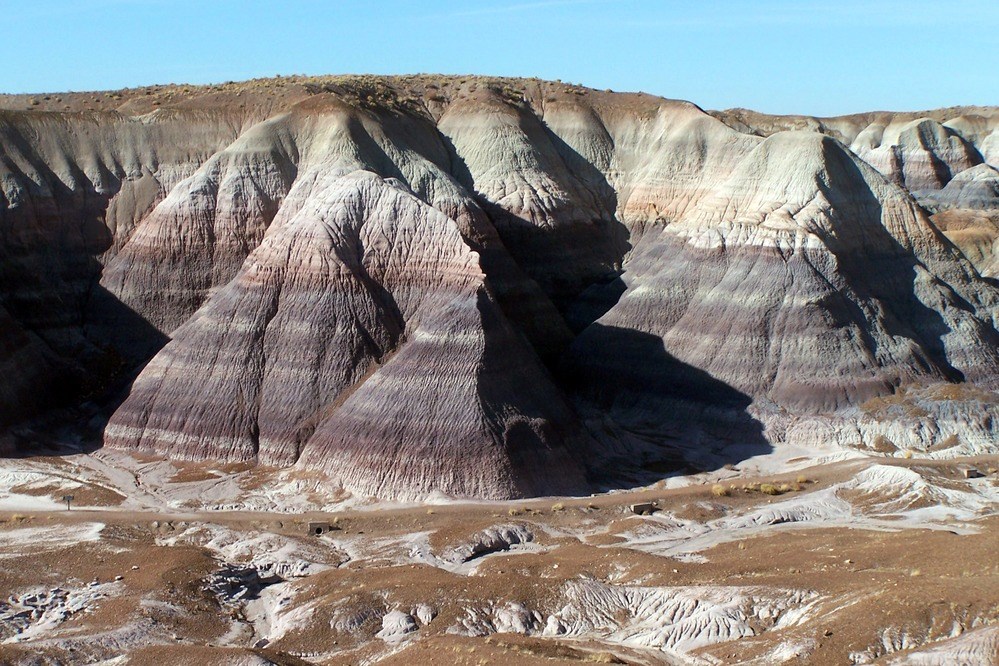

NPS Stratotype Inventory - Geology (U.S. National Park Service)
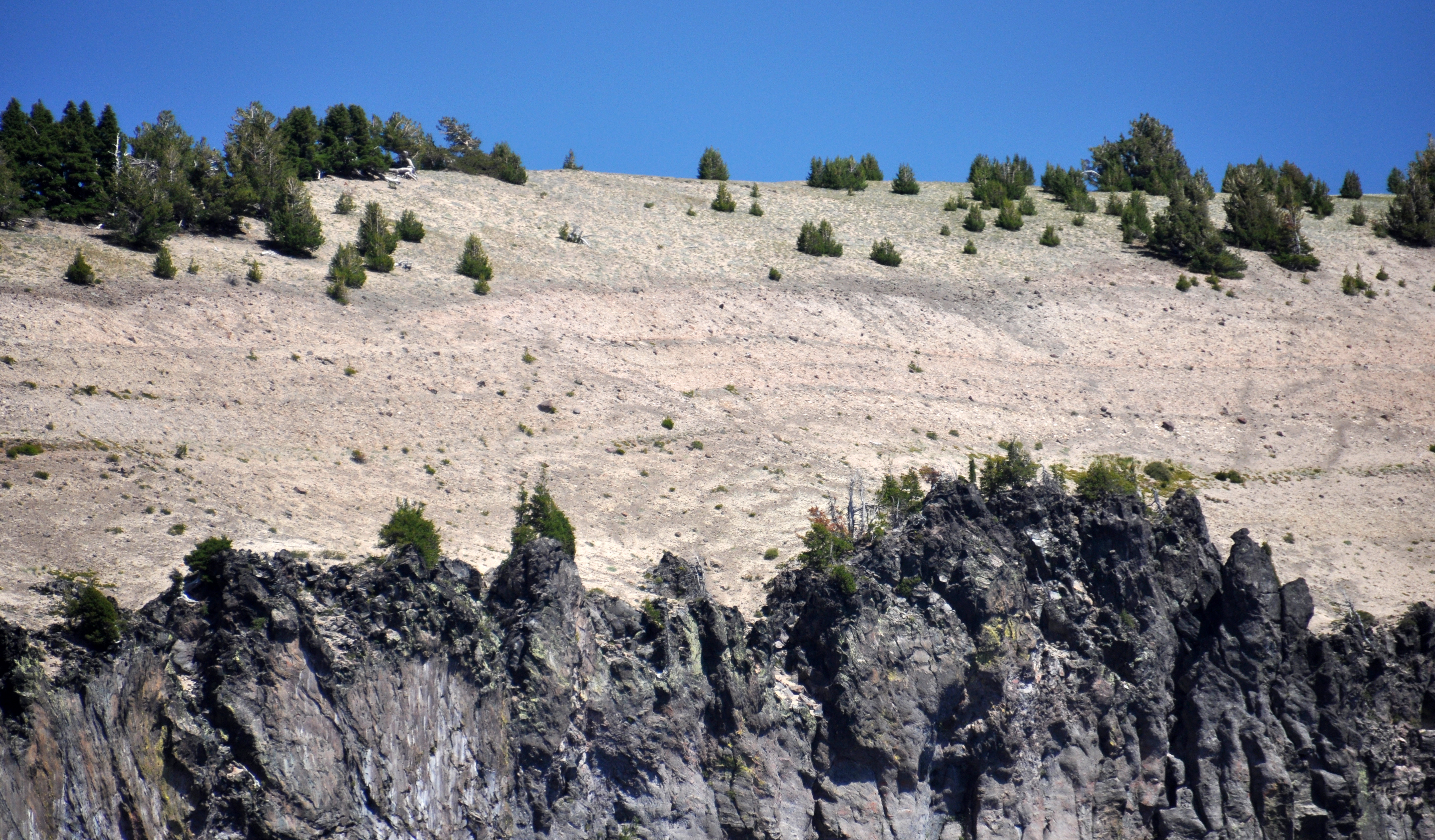

Volcanic Ash, Tephra Fall, and Fallout Deposits (U.S. National