Polymers, Free Full-Text
In order to synthesize a new kind of buoyancy material with high-strength, low-density and low-water-absorption and to study the curing reaction of tetraglycidylamine epoxy resin with an aromatic amine curing agent, the non-isothermal differential scanning calorimeter (DSC) method is used to calculate the curing kinetics parameters of N,N,N′,N′-tetraepoxypropyl-4,4′-diaminodiphenylmethane epoxy resin (AG-80) and the m-xylylenediamine (m-XDA) curing process. Further, buoyancy materials with different volume fractions of hollow glass microsphere (HGM) compounded with a AG-80 epoxy resin matrix were prepared and characterized. The curing kinetics calculation results show that, for the curing reaction of the AG-80/m-XDA system, the apparent activation energy increases with the conversion rates increasing and the reaction model is the Jander equation (three-dimensional diffusion, 3D, n = 1/2). The experimental results show that the density, compressive strength, saturated water absorption and water absorption rate of the composite with 55 v % HGM are 0.668 g·cm−3, 107.07 MPa, 0.17% and 0.025 h−1/2, respectively. This kind of composite can probably be used as a deep-sea buoyancy material.
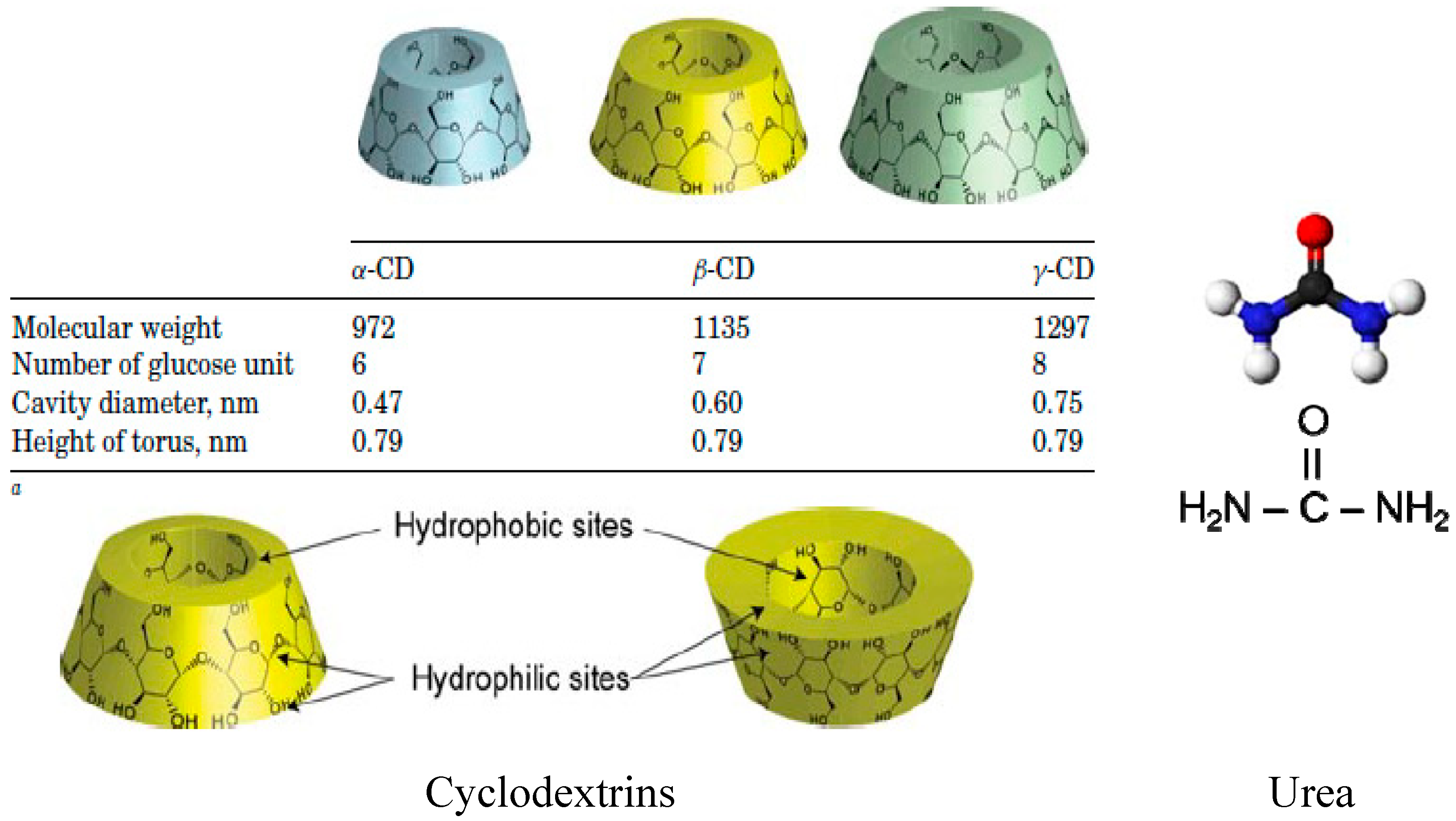
Polymers, Free Full-Text
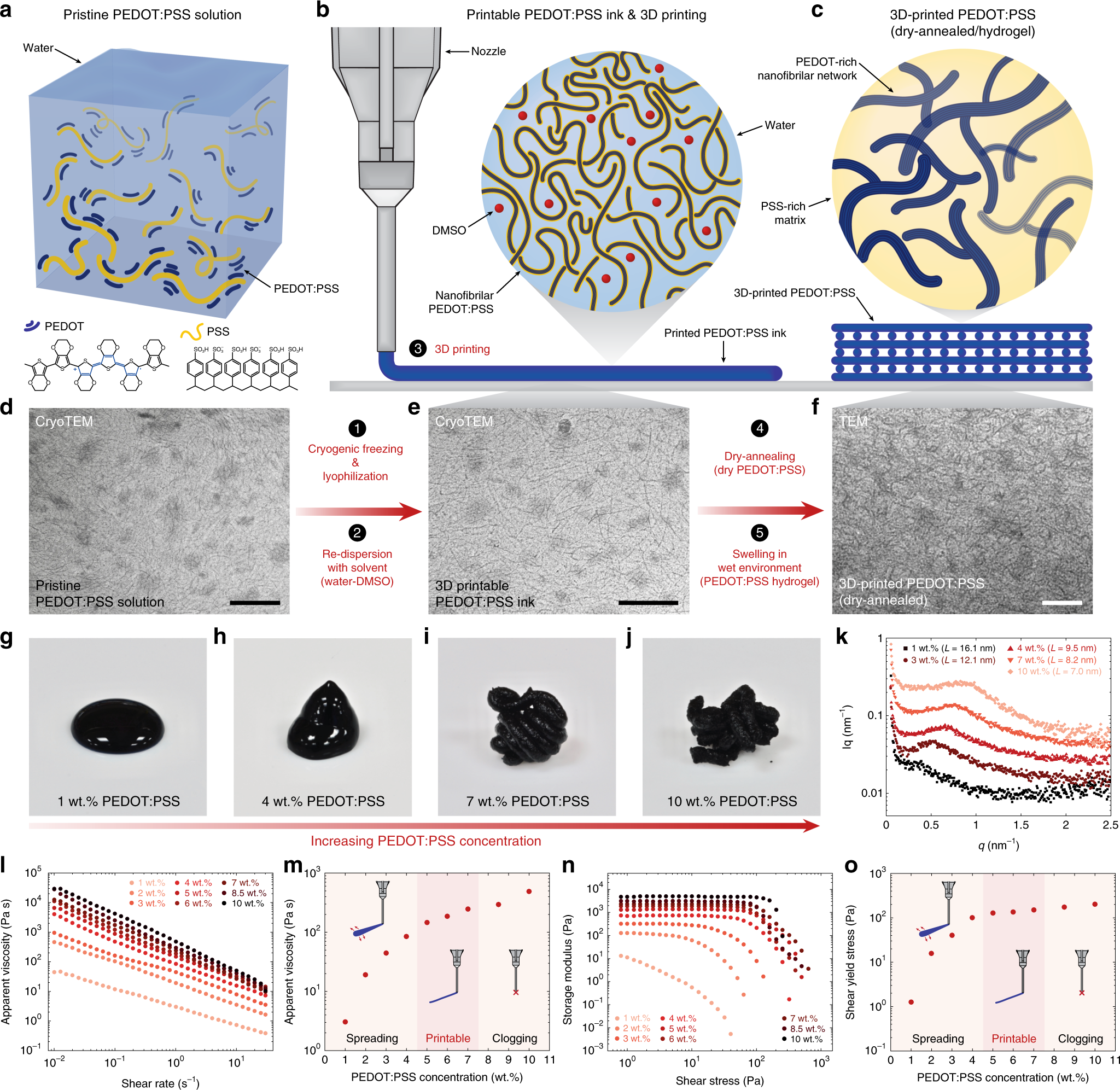
3D printing of conducting polymers
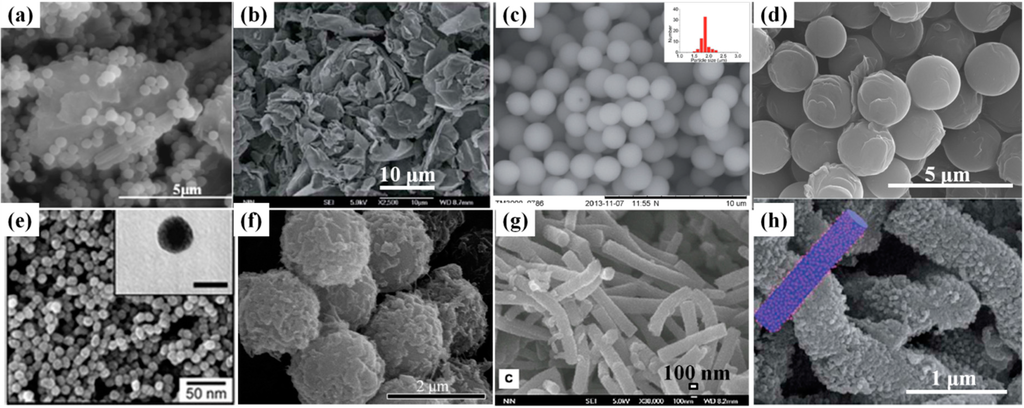

Polymers, Free Full-Text

Polymers, Free Full-Text

Polymers Free Full-Text Gelatin/Chitosan Bilayer Patches, 47% OFF

Free Radical Polymerization - Introduction, Mechanism

Polymer - Wikipedia
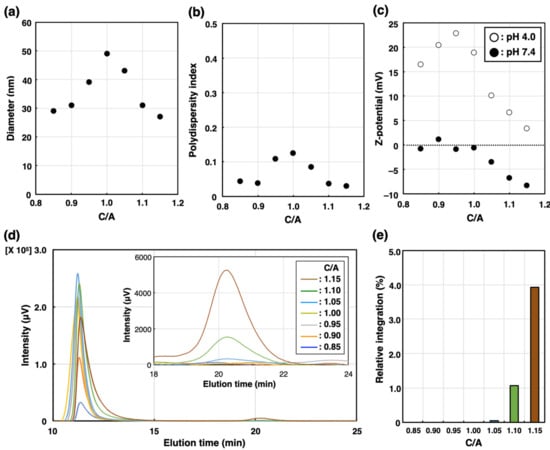
Raft 1.05 B Get File - Colaboratory
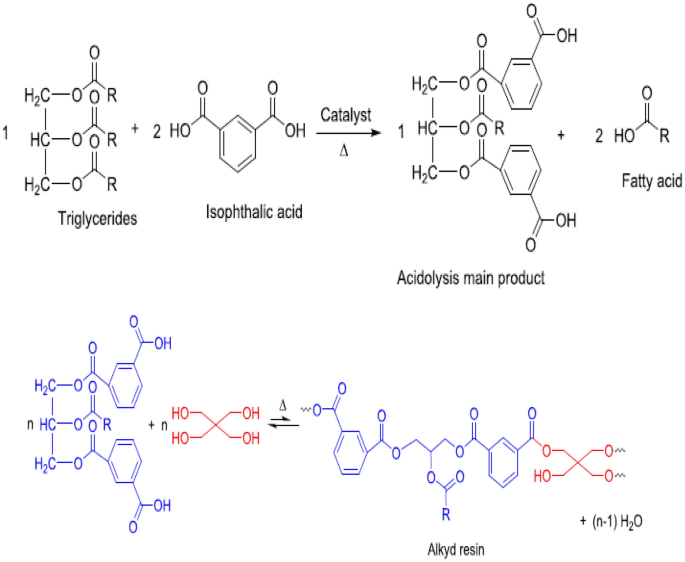
Waterborne Hybrid (alkyd/styrene Acrylic) Emulsion Polymers, 50% OFF
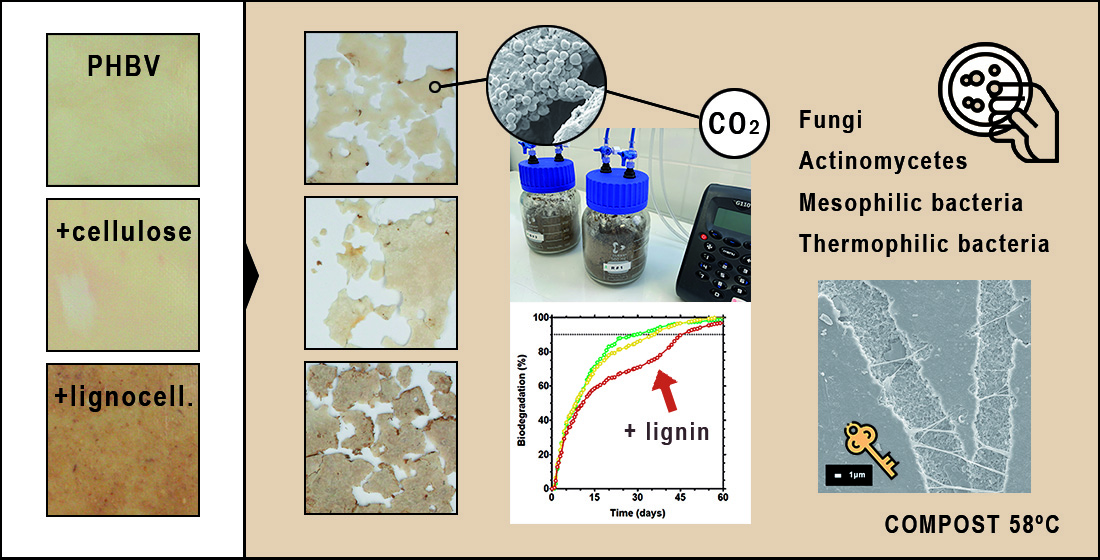
Polymers, Free Full-Text

Polymer Free Volume and Its Connection to the Glass Transition

Polymers, Free Full-Text