Electromagnetic Pulse
Effects of Nuclear Weapons. Electromagnetic pulse (EMP) is an electromagnetic wave similar to radio waves, which results from secondary reactions occurring when the nuclear gamma radiation is absorbed in the air or ground. It differs from the usual radio waves in two important ways. First, it creates much higher electric field strengths. Whereas a radio signal might produce a thousandth of a volt or less in a receiving antenna, an EMP pulse might produce thousands of volts. Secondly, it is a single pulse of energy that disappears completely in a small fraction of a second. In this sense, it is rather similar to the electrical signal from lightning, but the rise in voltage is typically a hundred times faster. This means that most equipment designed to protect electrical facilities from lightning works too slowly to be effective against EMP.

Bonding and microstructure evolution in electromagnetic pulse welding of hardenable Al alloys - ScienceDirect

Electromagnetic Pulse Threats to U.S. Expeditionary Operations in

Electromagnetic pulse, Wookieepedia

Study probes risks to power plants from electromagnetic pulse

Electro Magnetic Pulse Protection, Ministry of Defence

NEW 150MHz EMP Generator Hight-Power Electromagnetic Pulse Generator FAST SHIP

Electromagnetic Pulse: EMP Attack Survival Guide-Learn How To Prepare For And Survive An EMP Attack In Less Than 60 Minutes eBook : Johnson, James: Kindle Store
The Nuclear EMP Threat - How Electromagnetic Pulse Attacks Work
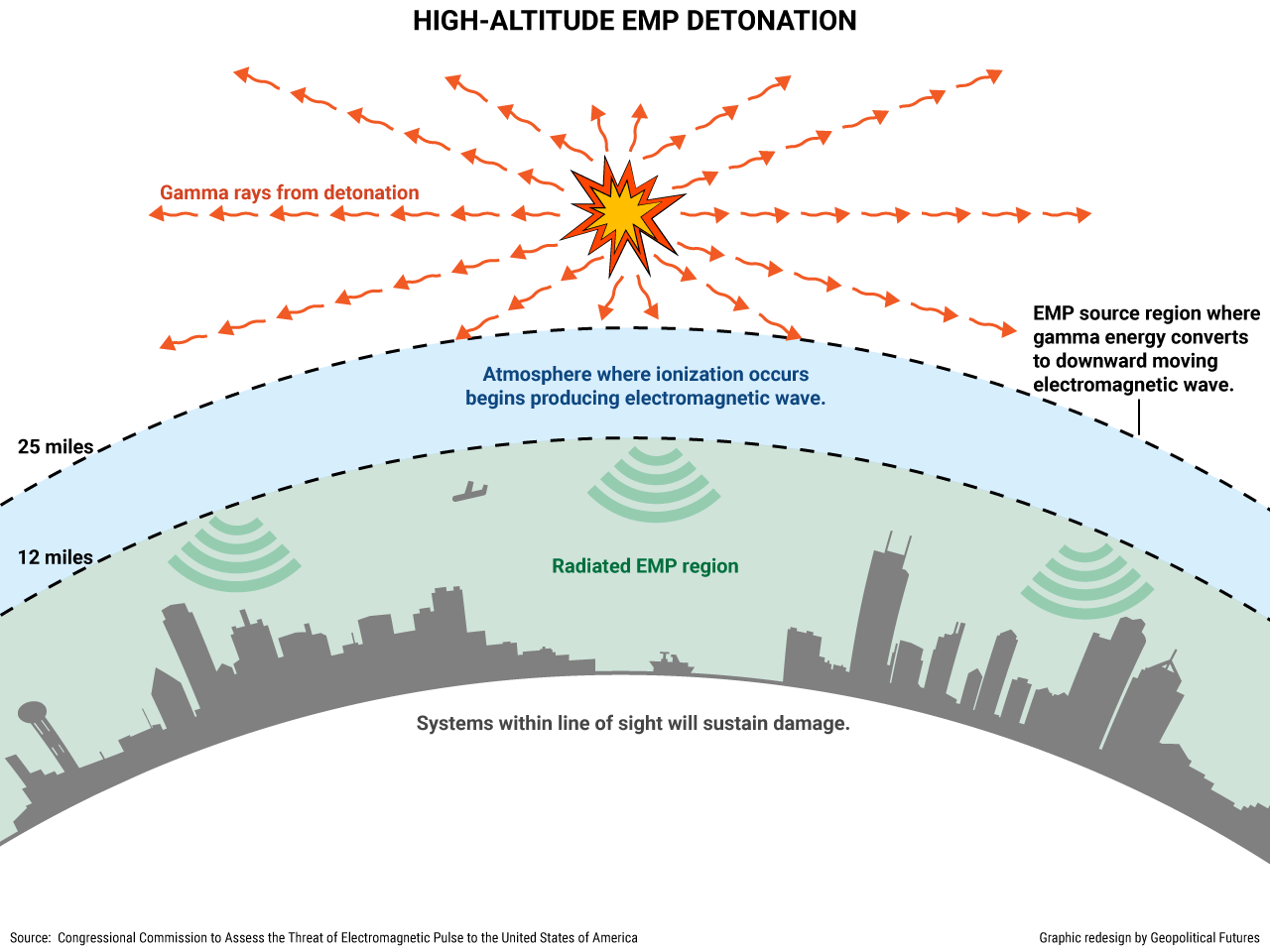
The EMP Threat: How It Works and What It Means for the Korean Crisis - Geopolitical Futures









