Chemical structure of three FAs, stearic acid C18:0 (top), oleic acid
Download scientific diagram | Chemical structure of three FAs, stearic acid C18:0 (top), oleic acid C18:1n9 (centre), and linolenic acid C18:3n3 (bottom); image source: chem.libretexts.org. from publication: The trophic reactor: a new concept of bioreactor and its application for the production of metabolites with commercial interest. | This dissertation presents a novel technology aimed at improving the economic feasibility of sourcing metabolites of commercial interest from microalgae. This technology consists of a continuous two-phase algae-crustacean bioreactor where a selected microalgae species is | Bioreactors, Metabolites and Zooplankton | ResearchGate, the professional network for scientists.
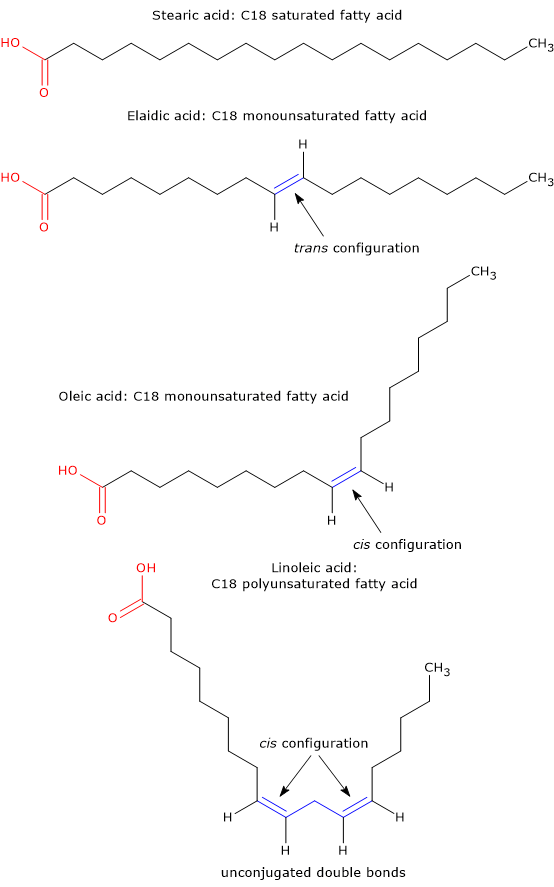
Fatty acids - Tuscany Diet

Chemical structure of three FAs, stearic acid C18:0 (top), oleic acid

Structure of TAG molecule. sn, Stereospecific numbering position; R

Fatty Acids and their Derivatives as Renewable Platform Molecules for the Chemical Industry - Biermann - 2021 - Angewandte Chemie International Edition - Wiley Online Library
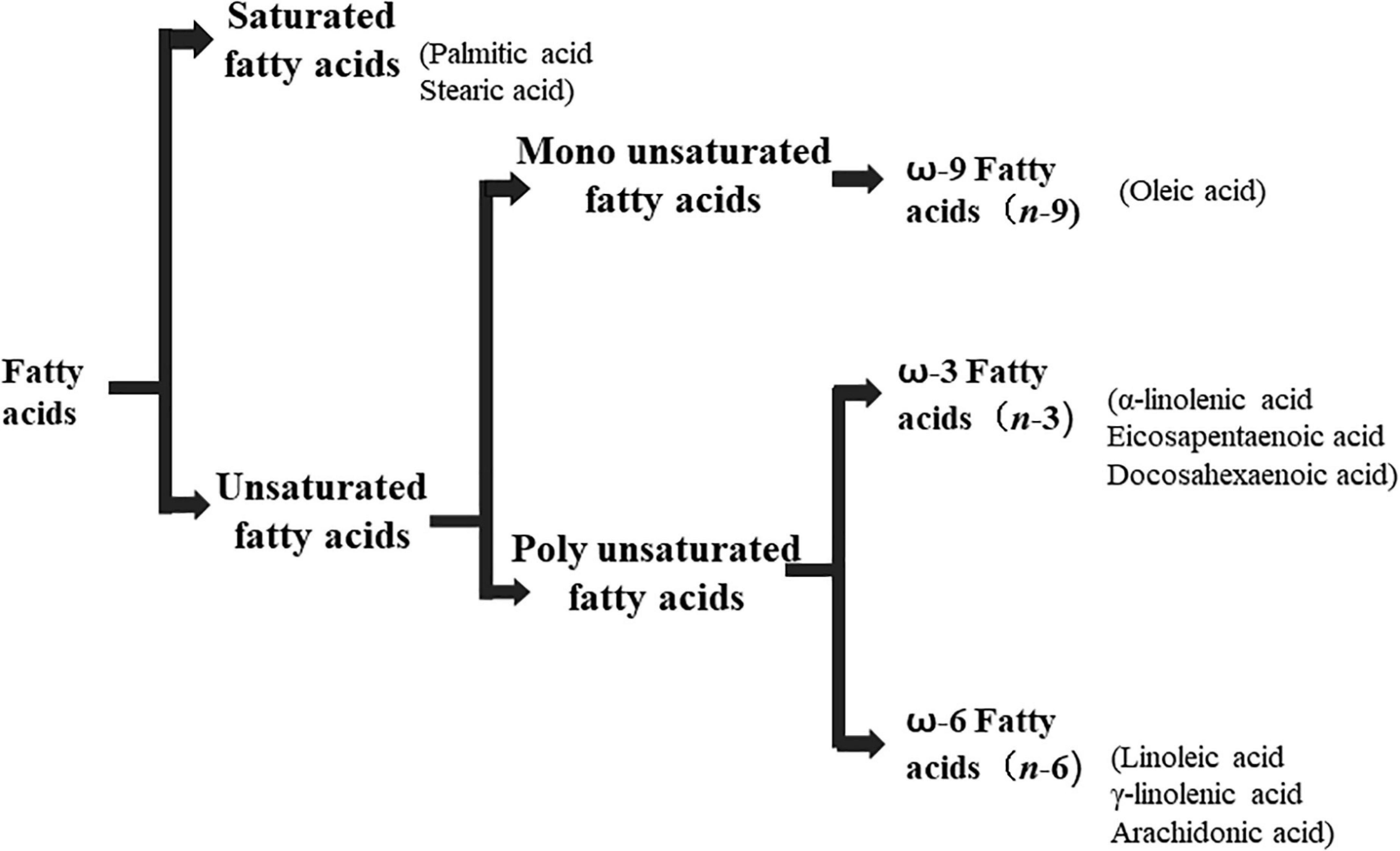
Frontiers Microbes: A Hidden Treasure of Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids

Variation of the stearic acid level (C18: 0) according to the individuals

Optimized Solid‐Phase‐Assisted Synthesis of Oleic Acid Containing siRNA Nanocarriers - Reinhard - 2017 - ChemMedChem - Wiley Online Library

JMSE, Free Full-Text
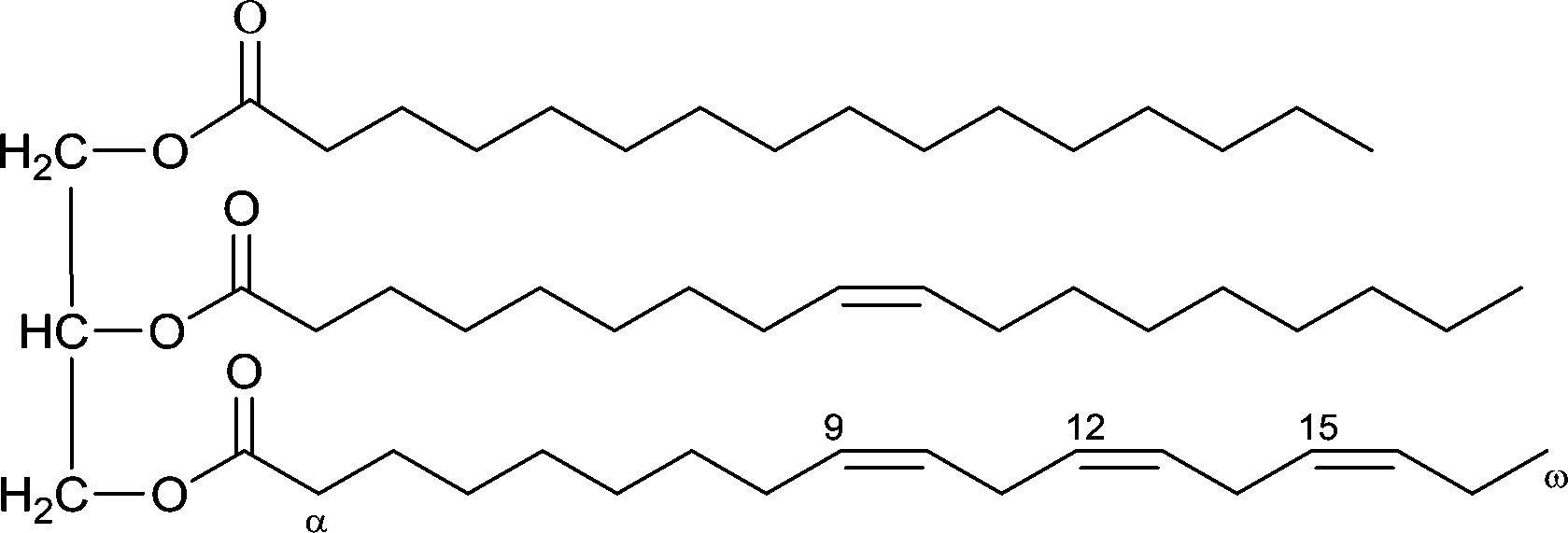
Chemically catalyzed oxidative cleavage of unsaturated fatty acids and their derivatives into valuable products for industrial applications: a review - Catalysis Science & Technology (RSC Publishing) DOI:10.1039/C5CY01118C
Stearic Acid, C18H36O2
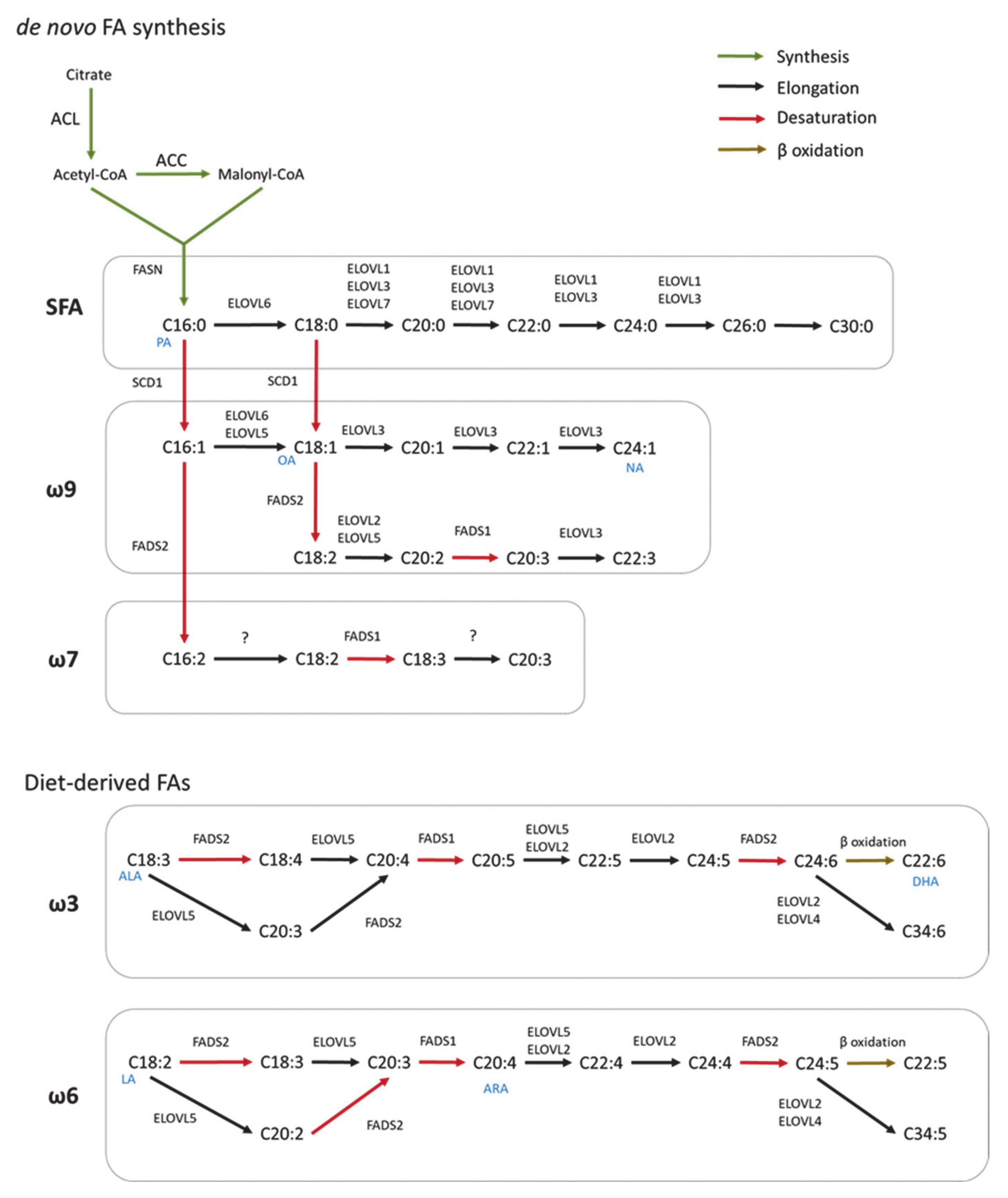
IJMS, Free Full-Text
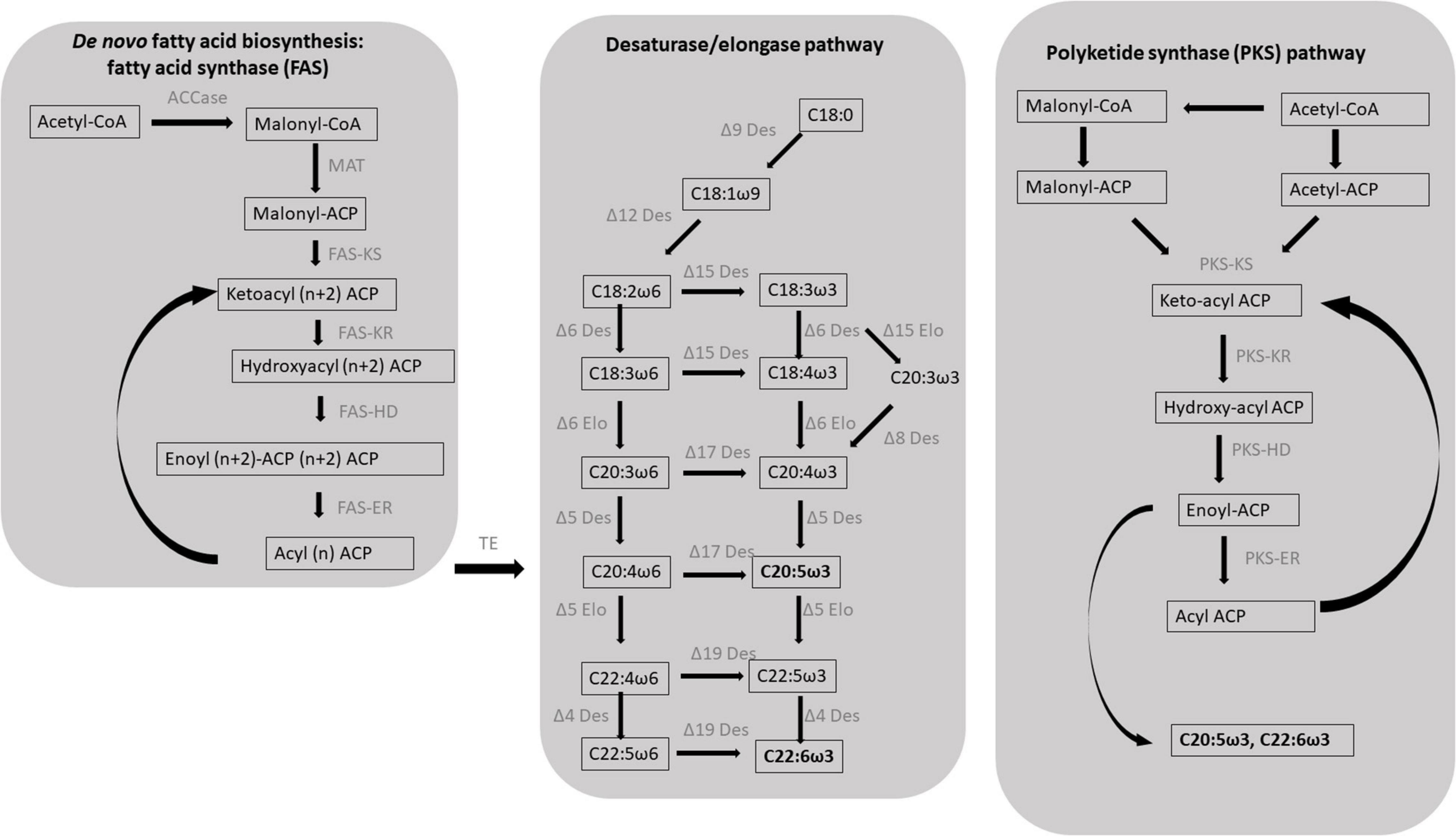
Frontiers Fatty Acids Derivatives From Eukaryotic Microalgae, Pathways and Potential Applications

Divergent evolution of extreme production of variant plant monounsaturated fatty acids








