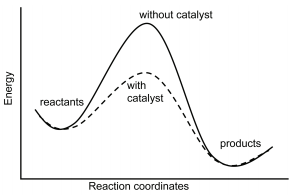
29.8: A Catalyst Affects the Mechanism and Activation Energy - Chemistry LibreTexts
Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions in which the catalyst is in solution with at least one of the reactants whereas heterogeneous catalysis refers to reactions in which the catalyst is present …
Homogeneous catalysis refers to reactions in which the catalyst is in solution with at least one of the reactants whereas heterogeneous catalysis refers to reactions in which the catalyst is present in a different phase, usually as a solid, than the reactants.
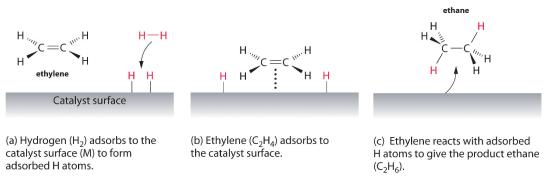
14.9: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts

Sequential Transformation of Terminal Alkynes to 1,3-Dienes by a Cooperative Cobalt Pyridonate Catalyst
How a catalyst lowers activation energy if it introduces a reaction pathway with many Ea? What if the sum of all these Ea is greater than the Ea of the uncatalysed reaction?

Principles of Chem 2

4.6 Catalysis – Inorganic Chemistry for Chemical Engineers
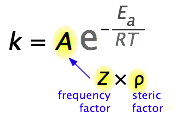
6.2.3.1: Arrhenius Equation - Chemistry LibreTexts

4.8: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts

Chapter 7 Flashcards

What does a catalyst do in chemical reactions? What role does activation energy play in chemical

6.10: Energies, Kinetics, and Catalysts - Chemistry LibreTexts

Hydrocracking of hydrotreated light cycle oil for optimizing BTEX production: a simple kinetic model
12.7: Catalysis - Chemistry LibreTexts
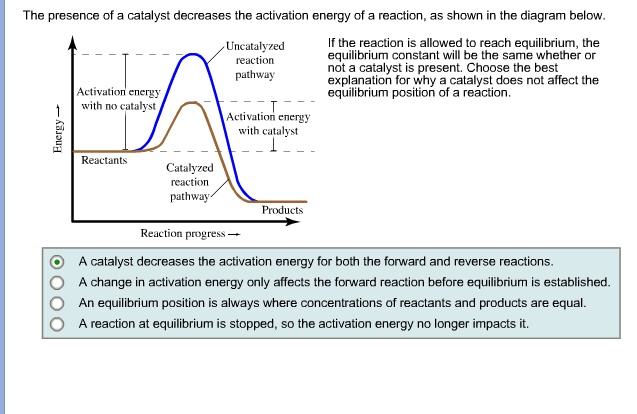
SOLVED: The presence of a catalyst decreases the activation energy of a reaction, as shown in the diagram below: Uncatalyzed [eiim pathway] If the reaction is allowed to reach equilibrium, the equilibrium

Hydrocracking of hydrotreated light cycle oil for optimizing BTEX production: a simple kinetic model








